Determination and Correlation of Solubilities of Benzoic Acid, Salicylic Acid, Resorcinol and Hydroquinone in Water and in 1-Octanol at Temperatures from 297.25 K to 334.45 K

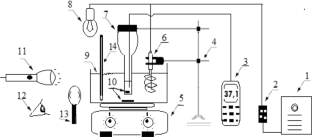
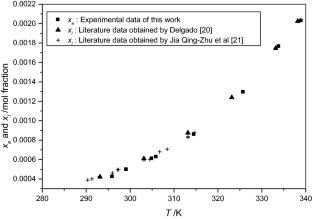
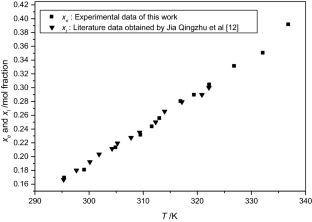
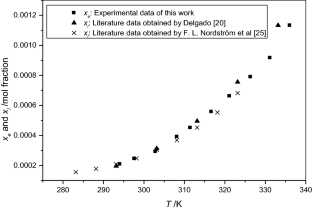
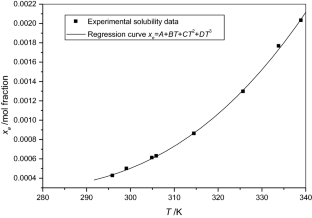
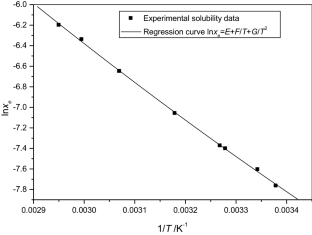
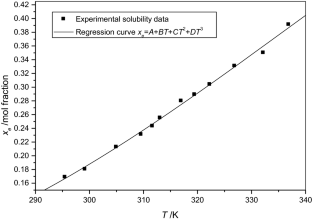
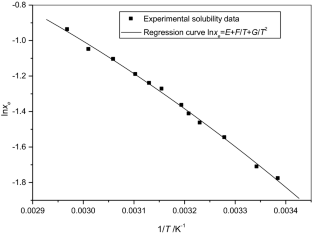
The solubilities of benzoic acid, salicylic acid, resorcinol and hydroquinone in water and in 1-octanol were measured by the dynamic method which is also called the synthetic method from 297.25 K to 334.45 K. Using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC Q2000 and SDT Q600), the melting temperature and the enthalpy of fusion of these solutes were determined. The obtained results show that the solubility of benzoic acid in water is greater than that of salicylic acid, but in the case of the two isomers of dihydroxybenzene, the solubility of resorcinol is approximately 100 times that of hydroquinone. In 1-octanol, the decreasing order of the solubility of these compounds is as follows: resorcinol > benzoic acid > salicylic acid > hydroquinone. The experimental solubilities were correlated using two regression equations. The correlation coefficient is greater than 0.9937 for one of these two equations for the binary studied systems where the solvent is either water or 1-octanol. New experimental data are provided for the solubility of resorcinol in water and salicylic acid, resorcinol, hydroquinone in 1-octanol.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve

Similar content being viewed by others
Salicylic Acid Solubility and Thermodynamic Dissociation Constant at Various Temperatures in Water: Variable Ionic Strength Titrimetric Analysis
Article 21 February 2024

Investigation of the solubility and thermodynamics of salicylic acid in 2-propanol and ethylene glycol/propylene glycol binary solvent mixtures at (293.15 to 313.15) K
Article Open access 09 May 2024

Solid-liquid phase equilibria, excess molar volume, and molar refraction deviation for the mixtures of ethanoic acid with propanoic, butanoic, and pentanoic acid
Article 05 June 2018
References
- C. M. S. de Mendonça, I. P. de Barros Lima, C. F. S. Aragão, A. P. B. Gomes, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 115, 2277–2285 (2014) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- A.-C. Huang, Y.-K. Chuang, C.-F. Huang, C.-M. Shu, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 132, 165–172 (2018) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- X. Li, Q. Yin, W. Chen, J. Wang, J. Chem. Eng. Data 51, 127–129 (2006) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J. Lim, S. Jang, H. K. Cho, M. S. Shin, H. Kim, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 57, 295–300 (2013) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- R. F. Pires, M. R. Franco Jr, Fluid Phase Equilib. 330, 48–51 (2012) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- A. Shalmashi, A. Eliassi, J. Chem. Eng. Data 53, 199–200 (2008) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- N. Sunsandee, S. Suren, N. Leepipatpiboon, M. Hronec, U. Pancharoen, Fluid Phase Equilib. 338, 217–223 (2013) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- S. H. Ali, F. S. Al-Mutairi, M. A. Fahim, Fluid Phase Equilib. 230, 176–183 (2005) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- A. Apelblat, E. Manzurola, N. A. Balal, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 38, 565–571 (2006) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- K. Carlsson, B. Karlberg, Anal. Chim. Acta 423, 137–144 (2000) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- S.-T. Lin, S. I. Sandler, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 38, 4081–4091 (1999) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J. Qingzhu, M. Peisheng, Y. Shouzhi, W. Qiang, W. Chang, L. Guiju, J. Chem. Eng. Data 53, 1278–1282 (2008) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- A. Van Haelst, P. Heesen, F. Van Der Wielen, H. Govers, Chemosphere 29, 1651–1660 (1994) ArticleADSGoogle Scholar
- W. J. Weber Jr, Y.-P. Chin, C. P. Rice, Water Res. 20, 1433–1442 (1986) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- G. Wienke, J. Gmehling, Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 65, 57–86 (1998) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Y.-H. Zhang, Trends Analyt. Chem. 15, 188–196 (1996) Google Scholar
- U. Domańska, Fluid Phase Equilib. 114, 175–188 (1996) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- I. Hahnenkamp, G. Graubner, J. Gmehling, Int. J. Pharm. 388, 73–81 (2010) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- H. Li, G. Hu, F. Guo, L. Zhao, J. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 88, 161–164 (2010) Google Scholar
- J. Delgado, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 43, 1311–1316 (2007) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J. Qing-Zhu, M. Pei-Sheng, Z. Huan, X. Shu-Qian, W. Qiang, Q. Yan, Fluid Phase Equilib. 250, 165–172 (2006) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- F. L. Mota, A. J. Queimada, A. E. Andreatta, S. P. Pinho, E. A. Macedo, Fluid Phase Equilib. 322, 48–55 (2012) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- K. Tamura, T. Kasuga, T. Nakagawa, Fluid Phase Equilib. 420, 24–29 (2016) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- W. E. Acree Jr, Thermochim Acta 189, 37–56 (1991) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- F. L. Nordström, Å. C. Rasmuson, J. Chem. Eng. Data 51, 1668–1671 (2006) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- C. L. Yaws, S.-C. Lin, Enthalpy of fusion at freezing point—Organic compounds, in Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons, William Andrew Publishing (Elsevier, 2009), pp. 552–591
- Z. Esina, M. Korchuganova, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 49, 313–321 (2015) ArticleGoogle Scholar
Funding
This study was funded by Ministère de l'Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- LSPS, Laboratoire de Spectrochimie Et Pharmacologie Structurale, University of Tlemcen, BP 119, 13000, Tlemcen, Algeria Boucif Belhachemi & Hamdi Makhlouf
- Department of Biology, University of Ghardaia, BP 455, 47000, Ghardaia, Algeria Mohammed Habib Belhachemi
- Boucif Belhachemi

















